hull
hull is used to create the convex hull of a set of constraints.
Syntax
F = hull(F1,F2,...)
Examples
Define two polytopes
sdpvar x y
F1 = [-1 <= x <= 1, -1 <= y <= 1];
F2 = [-1.5 <= x-y <= 1.5, -1.5 <= x+y <= 1.5];
Plot the polytopes
plot(F2);hold on
plot(F1);
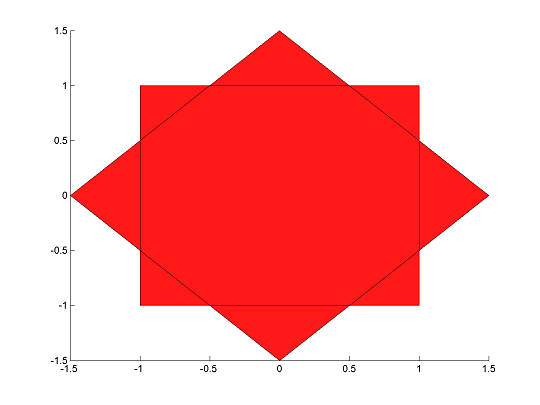
Create a model of the convex hull
H = hull(F1,F2)
+++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
| ID| Constraint| Type|
+++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
| #1| Numeric value| Element-wise 2x1|
| #2| Numeric value| Element-wise 2x1|
| #3| Numeric value| Element-wise 2x1|
| #4| Numeric value| Element-wise 2x1|
| #5| Numeric value| Equality constraint 2x1|
| #6| Numeric value| Equality constraint 1x1|
| #7| Numeric value| Element-wise 2x1|
+++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
Important to realize is that the representation will introduce new variables due to a lifting procedure. Nevertheless, YALMIP will realize that these are auxiliary variables defined internally, so when you plot the hull, the projection to the original user-defined variables will be plotted.
clf;
plot(H);hold on
plot(F2);
plot(F1);
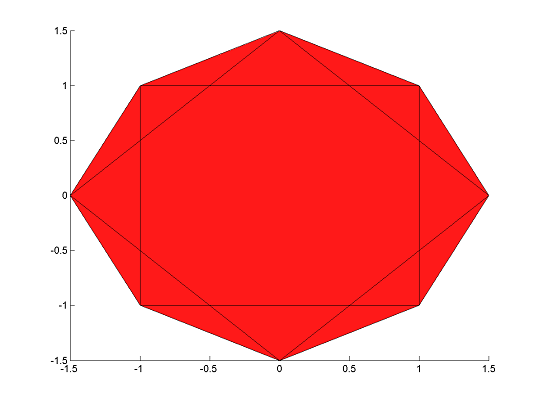
The command applies to (almost) arbitrary convex constraints.
clf;
sdpvar x y
F1 = [1 x y+3;[x;y+3] 1/5*eye(2)] >= 0];
F2 = [-1.5 <= x-y <= 1.5,-1.5 <= x+y <= 1.5];
H = hull(F1,F2);
plot(H,[x y]);hold on
plot(F2);
plot(F1);
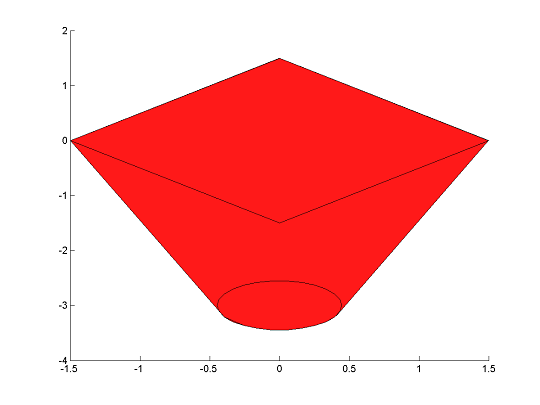
At the moment, the command does not support constraints that involve nonlinear expression (beyond quadratic or graph-represented).
